Wide area network or WAN. The IP address belonging to Class A uses only the first octet to identify the network and the last three octets are used to identify the host.
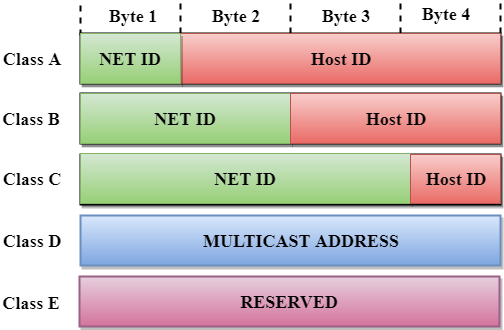
The length of network addresses and host addresses in IP addresses are different in all IP classes.

. Class D is for multicasting. So a class A network of 10xxx would have MANY addresses 2543 available to assign. It is used for medium size networks.
And class E is rarely used at all within networks of companies. A B C D and E. Metropolitan area network or MAN.
The remaining 24 bits are available for the host address. It opens doors to new opportunities. Class E is experimental so you can just forget about those too.
These classes are class A class B and class C. The default subnet mask for Class B is 255255xx. In this class three octets are used to indent the network.
Subnetting needs a specialist to implement it properly and effectively. In this part we will see four different Subnetting ExamplesWith these Subnetting Examples you will learn this lesson very well. Class A networks accounts for half of the total available IP addresses.
Also known as Cluster Area Network. A class A network number uses the first eight bits of the IP address as its network part. Network addresses for these range from 128 to 191.
Choose any one Hazardous items from different class. Class C is a type of IP address that is used for the small network. The Class A subnet mask is 255000.
Each class gives you less total addresses to assign to devices. Class of Service CoS is a way of managing traffic in a network by grouping similar types of traffic for example e-mail streaming video voice large document file transfer together and treating each type as a class with its own level of service priority. Class D is for multicast addresses which is something else entirely.
The first octet of Class C IP address has its first 3 bits set to 110. Class C amplifier is tuned amplifier which works in two different operating modes tuned or untuned. The Host ID has 24 bits.
Class B networks have a first bit value of 1 and a second bit value of 0 in the first octet. The range of IP addresses is 128000 to 191255255255. For example for the small number of networks with a very large number of hosts the Class A was created.
The Network ID has 8 bits. Subnetting Examples. The system of IP address classes was developed for the purpose of Internet IP addresses assignment.
Maximum 80 efficiency can be achieved in radio frequency related operations. Unlike Quality of Service QoS traffic management Class of Service technologies. In class A the first bits are reserved for the network address.
The default subnet mask for Class A IP address is 255000. Class B has 16384 2 14 Network addresses and 65534 2 16-2 Host addresses. Why Transportation Safety is of critical importance now a days.
In this type of network addressing method the first two bits are set to be 1 and the third bit is set to 0 which makes the first 24 bits of the address them and the remaining bit as the host. Some of the different networks based on size are. An example is 1234567891.
Personal area network or PAN. Class A Network Numbers. In this example the server is hosted on the 789 C block and has a unique value that.
Class B IP Addresses range from 1280xx to 191255xx. In the first one of the Subnetting Examples we will use 192168585 24 AddressLets determine the network and host part of this addressThis is the first example so. Local Area Network LAN Metropolitan Area Network MAN Wide Area Network WAN Local area network LAN LAN is a computer network that consists of few or more computers and other communication devices connected in the form of a network within a well-defined area such as.
However in laymans terms IP classes range from A - E. The IP address with a first octet from 128 to 191 is part of this class. The classes created were based on the network size.
In comparison to Class A Class B IP addresses are better suited to serving smaller networks since they reserve 14 bits for a network which leaves only 18 bits for hosts. Explain reasons with suitable examples from GCC and Oman in particular. Based on geographical spread networks can be classified into the following three categories.
One of the main reasons for this is the different opportunities that you discover through networking which you would have otherwise never seen or thought of before. This course is dedicated to understanding the fundamentals of carrier packet networks and services and the terminology configuration and operation of specific technologies including Frame Relay and most importantly MPLS. The first bit of the first octet is always set to 0.
The IP protocol defines five different address classes. Carrier Packet Networks Technologies MPLS SLAs CoS Integration Aggregation. In class B the first 16 bits are reserved for the network address while the last 16 bits are.
Explain reasons with suitable examples from GCC and Oman in particular. Class C amplifier uses less than 180-degree conduction angle. System Area Network - links high-performance computers with high-speed connections in a cluster configuration.
IP classification is complex. Class A B and C are used for host addresses without exception. This IP ranges between 192 to 223.
This means that it allows 214 networks and 216 hosts per network. In terms of purpose many. The first three classes vary the portion of the address devoted to the network ID and the host ID.
The efficiency of Class C amplifier is much more than the A B and AB. Class B would be less 1010xx 2542 and Class C 101010x only 254 maximum. ADVANTAGES OF COMPUTER NETWORKS File Sharing.
Currently there are three classes of TCPIP networks. Class B IP address always has its first bits as 10 next 14 bits as a network address and following 16 bits as the host address. Accordingly Class A IP addresses are best used to serve incredibly large networks.
Up to 24 cash back Storage Area Network - connects servers to data storage devices through a technology like Fibre Channel. Class C Network. Class B IP address format is.
Explain its transportation process using a suitable diagram. Each class uses the 32-bit IP address space differently providing more or fewer bits for the network part of the address. A LinkedIn study found that 80 of professionals consider networking important for their career success.
The C Class IP addresses always contain four unique blocks. Search Engine Optimization SEO hosting with Class C network address is a straightforward form of hosting services that uses different C Class IP hosting addresses. Class C is used for small to middle size networks.
The Class C was created for numerous networks with small number of hosts. Local area network or LAN. This class of IP address is used for a medium network like multinational companies.

Ip Addressing And How It Works Tech Apps Networking Computer Network

0 Comments